

Now to be clear, that's 1000 Megabits (Mb) not Megabytes (MB). The units are aggregated in powers of 2, specifically 2 10.1Gbps is 1,000Mbps, or 1000 Megabits per second, which is really really fast. Similarly Mi stands for Mebi, Gi for Gibi, and Ti for Tebi. Ki stands for kibi, so KiB/s is kibibytes per second while Kib/s or Kibit/s is kibibit per second.These units are aggregated in multiples of 1000.

M stands for mega, G for giga, T for tera.
K stands for kilo and may be used in upper or lower case. MB/s is megabyte per second and Mbps is megabit per second. Use lower-case b for bits and upper-case B for bytes. For example, Kilobits per second uses the symbol kbps, kbit/s or kb/s Kilobytes per second is written as kB/s and Mbps stands for Megabit per second. 1024 is 2 10.ĭata rate units are represented as information per second. Since computing uses a binary system, the totals for units of storage are always in powers of 2. Kibi-, mebi-, gibi-, tebi-, pebi-:these prefixes denote aggregations in units of 1024. They denote aggregations in units of 1,000. Kilo-, mega-, giga-, tera-, peta-: these are the prefixes most widely used. The suffix denotes whether the unit is representing bits or bytes the prefix denotes how many bits/bytes are being conveyed. All other units of information are derived from bits and bytes, and represent a certain number of bits (or bytes).Įach unit contains a prefix and suffix. 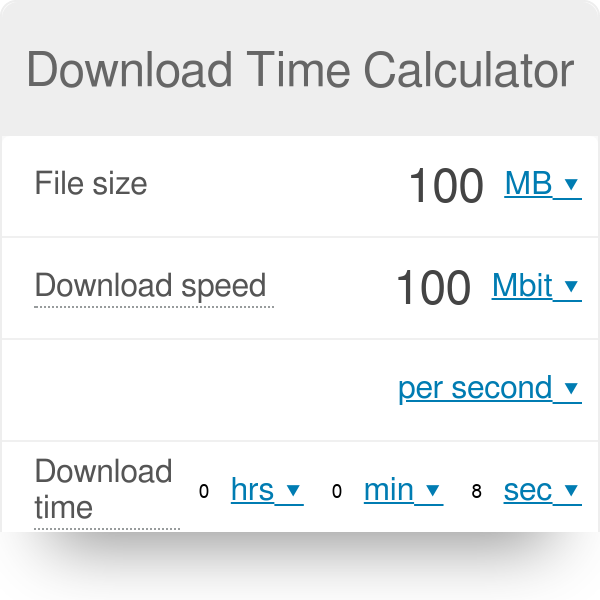
A byte is the next smallest unit, and is equal to 8 bits. File sizes are usually expressed in KB and MB whereas kb and Mb are often used to express data transfer speeds (such as a 54 Mbps wireless router or 3G or 4G connection speeds).Ī bit is the smallest unit of information. While MB is megabytes, Mb refers to Megabits.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
